Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Luo, G.; Shu, Wataru; Nishi, Masataka
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 347(1-2), p.111 - 117, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:85 Percentile:98.14(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Polycrystalline tungsten samples have been irradiated at room temperature by high flux (1 10
10 D/m
D/m /s) deuterium plasma beams with incident energies ranging 7
/s) deuterium plasma beams with incident energies ranging 7  98 eV/D. Surface blistering occurred at all energies. The critical fluence for blistering
98 eV/D. Surface blistering occurred at all energies. The critical fluence for blistering 
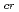 was found to increase with decreasing the incident energy. At energies
was found to increase with decreasing the incident energy. At energies  20 eV/D,
20 eV/D, 
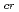 increased more rapidly. This energy dependence of
increased more rapidly. This energy dependence of 
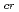 may be explained by a proposed model dealing with the oxide barrier to deuterium uptake into and release from the bulk W. At all energies, the blisters increased in their size and number with fluence within the corresponding low fluence ranges. However the size stopped increasing at certain fluences, while the number kept increasing within the experimental fluence range, which could be attributed to rupturing of blisters at a certain size of about 2
may be explained by a proposed model dealing with the oxide barrier to deuterium uptake into and release from the bulk W. At all energies, the blisters increased in their size and number with fluence within the corresponding low fluence ranges. However the size stopped increasing at certain fluences, while the number kept increasing within the experimental fluence range, which could be attributed to rupturing of blisters at a certain size of about 2 m.
m.
Sasaki, Masayoshi*; Morimoto, Yasutomi*; Kimura, Hiromi*; Takahashi, Koji; Sakamoto, Keishi; Imai, Tsuyoshi; Okuno, Kenji*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 329-333(Part1), p.899 - 903, 2004/08
A CVD diamond has been the reference material of a torus widow for a rf heating system in a fusion reactor. Since the window is in the circumstance of tritium, helium and radio activated dust, it is important to elucidate the effect of ions on chemical structure of the diamond, existing states of tritium and tritium inventory. Polycrystalline CVD diamond disks( =10.0mm, t=0.21mm) used in this study are the same grade as rf windows. After sputtering the surface with 1.0 keV Ar
=10.0mm, t=0.21mm) used in this study are the same grade as rf windows. After sputtering the surface with 1.0 keV Ar to remove oxygen impurity, the sample was irradiated with deuterium (D
to remove oxygen impurity, the sample was irradiated with deuterium (D
 ) or helium ions (He
) or helium ions (He ) at an angle of 0 degrees to the surface normal. The irradiation energies of deuterium and helium are 0.25 keV D
) at an angle of 0 degrees to the surface normal. The irradiation energies of deuterium and helium are 0.25 keV D and 0.45 keV He
and 0.45 keV He , respectively. The structural change of the irradiated sample was measured by X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) technique. The C1s peak shift toward lower binding energy side was observed when deuterium ions irradiated. This result indicates that the diamond changes to amorphous carbon due to formation of C-D bond.
, respectively. The structural change of the irradiated sample was measured by X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) technique. The C1s peak shift toward lower binding energy side was observed when deuterium ions irradiated. This result indicates that the diamond changes to amorphous carbon due to formation of C-D bond.
Sugie, Tatsuo; Kasai, Satoshi; Taniguchi, Masaki; Nagatsu, Masaaki*; Nishitani, Takeo
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 329-333(2), p.1481 - 1485, 2004/08
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:85.88(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In ITER, the effect of lower energy particle bombardment is important for mirrors located near the divertor where the low temperature plasma is formed. The test pieces of molybdenum mirrors and a tungsten mirror were irradiated by high flux and low energy (67-80 eV) deuterium ions using SLEIS (Super Low Energy Ion Source with High Ion Flux) facility at the temperature of around 100  C. The molybdenum mirror manufactured by sintering and melting the thin layer of the surface by electron beam in order to eliminate holes on the surface has a higher reflectivity before irradiation than the mirrors without melting the surface, but the reflectivity decreases rapidly with the irradiation fluence due to the generation of blisters on the mirror surface. The reflectivity of molybdenum mirror manufactured by sintering only did not decrease so significantly (less than 10 % at the fluence of 1.3
C. The molybdenum mirror manufactured by sintering and melting the thin layer of the surface by electron beam in order to eliminate holes on the surface has a higher reflectivity before irradiation than the mirrors without melting the surface, but the reflectivity decreases rapidly with the irradiation fluence due to the generation of blisters on the mirror surface. The reflectivity of molybdenum mirror manufactured by sintering only did not decrease so significantly (less than 10 % at the fluence of 1.3  10
10 m
m ). The molybdenum and tungsten mirrors manufactured by sintering without melting the surface have a potential for plasma facing mirrors in ITER.
). The molybdenum and tungsten mirrors manufactured by sintering without melting the surface have a potential for plasma facing mirrors in ITER.
Igarashi, Shinichi; Muto, Shunsuke*; Tanabe, Tetsuo*; Aihara, Jun; Hojo, Kiichi
Surface & Coatings Technology, 158-159, p.421 - 425, 2002/09
no abstracts in English
JAERI-M 7154, 15 Pages, 1977/07
no abstracts in English